The Entity/Relationship Model
The Entity/Relationship Model
- Introduction to the Entity-Relationship (E/R) model, which represents the structure of data graphically as an entity-relationship diagram.
- Identifies the three principal element types of the E/R model: Entity sets, Attributes, and Relationships.
#1
read: Section 4.1: The Entity/Relationship Model (section)
model: pro
rules: bullet definition math presentation short
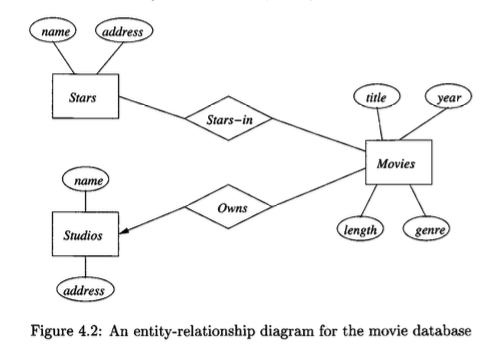
Short intro paragraph.The Entity/Relationship (E/R) model provides a high-level, graphical representation for the structure of data. It is a conceptual design tool used to model the information that a database will contain. The model is constructed from three principal element types: entity sets, attributes, and relationships.
Definition: Entity/Relationship Model
An Entity/Relationship model describes data in terms of:
- A collection of entity sets, \(\mathcal{E} = \{E_1, E_2, \dots, E_n\}\).
- A collection of relationship sets, \(\mathcal{R} = \{R_1, R_2, \dots, R_m\}\).
- A set of attributes associated with each entity set and relationship set.
- A set of constraints, such as multiplicity, that govern the relationships between entity sets.
Entity Sets
An entity is an abstract, distinguishable object. An entity set is a collection of similar entities. An entity set is analogous to a class in object-oriented programming, but it is a static concept concerned only with data structure, not operations. Entity sets are represented by rectangles in E/R diagrams.
Attributes
Attributes are properties of the entities within an entity set. In the standard E/R model, attributes are of primitive types, such as integers or strings. Attributes are represented by ovals, connected by an edge to their corresponding entity set.
Relationships
A relationship is an association among two or more entity sets. An instance of a relationship is a tuple of entities, one from each of the associated entity sets. Relationships are represented by diamonds, connected by edges to the entity sets they involve.
Entity-Relationship Diagrams
An E/R diagram is a graphical representation of an E/R model. The diagram uses specific shapes for each component:
- Rectangles: Represent entity sets.
- Ovals: Represent attributes.
- Diamonds: Represent relationships. Edges connect these components to show their associations.
Multiplicity Constraints
Constraints on binary relationships specify the number of entities from one set that can be related to an entity in another set. Arrows on the edges of an E/R diagram indicate these constraints. An arrow pointing from a relationship to an entity set \(E\) signifies a “many-one” constraint, meaning each entity in the other participating set(s) can be related to at most one entity in \(E\).
- Many-to-One: An arrow to one entity set.
- One-to-One: An arrow to both entity sets.
- Many-to-Many: No arrows.
Roles
An entity set may participate in a single relationship more than once, in different capacities or “roles.” In such cases, the edges connecting the relationship to the entity set are labeled to distinguish these roles. A common example is a
Sequel-ofrelationship on aMoviesentity set, with roles for theoriginalandsequelmovie.Subclasses and
isaRelationshipsAn entity set may contain a subgroup of entities with special attributes or relationships. This subgroup can be modeled as a subclass, connected to its superclass by a special
isarelationship. Theisarelationship is one-to-one and is represented by a triangle in the E/R diagram, with the point of the triangle directed at the superclass.
- Version: 1
- Model: gemini-2.5-pro
- Created: 2025-09-09 21:18:32
- Duration: 26.019952297210693
- Cummulative cost: $2.78e-02
Entity Sets
- Defines an entity as an abstract object and an entity set as a collection of similar entities, analogous to objects and classes in object-oriented programming.
- Notes that the E/R model is a static concept focused on data structure, not operations.
#2
read: Section 4.1.1: Entity Sets (section)
model: pro
rules: bullet definition math presentation short
Present the following. Use definition formal definition when it applies.
- Defines an entity as an abstract object and an entity set as a collection of similar entities, analogous to objects and classes in object-oriented programming.
- Notes that the E/R model is a static concept focused on data structure, not operations.
Definition: Entity Set
An entity is an abstract object of some sort. A collection of similar entities forms an entity set.
An entity set is analogous to a class in object-oriented programming, and an entity is analogous to an object.
For example, in a movie database, the set of all movies constitutes an entity set. Each individual movie is an entity within that set.
The Entity-Relationship model is a static concept.
It describes the structure of data, not the operations on the data. Consequently, one does not associate methods with an entity set as one would with a class.
- Version: 1
- Model: gemini-2.5-pro
- Created: 2025-09-09 21:20:27
- Duration: 9.091724157333374
- Cummulative cost: $1.09e-02
Attributes
- Defines attributes as properties of the entities within an entity set.
- Assumes attributes are of primitive types like strings or integers, though variations exist.
#3
read: Section 4.1.2: Attributes (section)
model: pro
rules: bullet definition math presentation short
Present the following. Use definition formal definition when it applies.
- Defines attributes as properties of the entities within an entity set.
- Assumes attributes are of primitive types like strings or integers, though variations exist.
Definition: Attribute
An attribute is a property of the entities in an entity set. For a given entity set, each entity is described by the values of the attributes associated with that set.
Entity sets have associated attributes.
These attributes represent the properties of the entities within that set. For instance, the entity set
Moviesmight be given attributes such astitleandlength.Attributes are of primitive types.
In our discussion, we shall assume that attributes are of simple, primitive types, such as strings, integers, or reals. More complex variations of the E/R model exist that permit structured attributes, such as composite types (structs) or sets of values.
- Version: 1
- Model: gemini-2.5-pro
- Created: 2025-09-09 21:32:39
- Duration: 8.911308765411377
- Cummulative cost: $1.31e-02
Relationships
- Defines relationships as connections among two or more entity sets.
- Introduces binary relationships as the most common type but notes that the E/R model allows relationships to involve any number of entity sets.
#4
read: Section 4.1.3: Relationships (section)
model: pro
rules: bullet definition math presentation short
Present the following. Use definition formal definition when it applies.
- Defines relationships as connections among two or more entity sets.
- Introduces binary relationships as the most common type but notes that the E/R model allows relationships to involve any number of entity sets.
Definition: Relationship
A relationship is a connection among a list of \(n\) entity sets \(E_1, E_2, \ldots, E_n\). An instance of the relationship is a set of tuples \((e_1, e_2, \ldots, e_n)\) where each \(e_i\) is an entity from the corresponding entity set \(E_i\).
Relationships are connections established between two or more entity sets.
For example, if
MoviesandStarsare two entity sets, a relationshipStars-incan connect movies to the stars that act in them. An instance of this relationship would be a pair, such as (Total Recall,Arnold Schwarzenegger), connecting a specific movie entity to a specific star entity.While the most common type of relationship is binary, connecting two entity sets, the E/R model is more general.
The model permits relationships to involve any number of entity sets. These are referred to as multiway relationships. For instance, a ternary relationship might connect three entity sets, such as
Studios,Stars, andMovies.
- Version: 1
- Model: gemini-2.5-pro
- Created: 2025-09-09 21:34:22
- Duration: 11.724592685699463
- Cummulative cost: $1.47e-02
Entity-Relationship Diagrams
- Describes an E/R diagram as a graph representing entity sets, attributes, and relationships.
- Specifies the graphical notation: rectangles for entity sets, ovals for attributes, and diamonds for relationships.
#5
read: Section 4.1.4: Entity-Relationship Diagrams (section)
model: pro
rules: bullet definition math presentation short
Present the following. Use definition formal definition when it applies.
- Describes an E/R diagram as a graph representing entity sets, attributes, and relationships.
- Specifies the graphical notation: rectangles for entity sets, ovals for attributes, and diamonds for relationships.
Definition: Entity-Relationship Diagram
An Entity-Relationship (E/R) diagram is a graph that represents the logical structure of a database. It visually portrays entity sets, their attributes, and the relationships among them.
The graphical notation employs three principal element types, each represented by a distinct shape:
Entity Sets
Entity sets are represented by rectangles. An entity set is a collection of similar entities, analogous to a class in object-oriented programming.
Attributes
Attributes are represented by ovals. These are properties of the entities within an entity set. Edges connect attributes to their corresponding entity set.
Relationships
Relationships are represented by diamonds. These nodes represent connections among two or more entity sets. Edges connect the relationship diamond to the entity sets it involves.
- Version: 1
- Model: gemini-2.5-pro
- Created: 2025-09-09 21:34:31
- Duration: 8.80923318862915
- Cummulative cost: $1.07e-02
Instances of an E/R Diagram
- Explains the concept of a database instance for an E/R diagram, which consists of a finite set of entities for each entity set and a set of tuples (the relationship set) for each relationship.
#6
read: Section 4.1.5: Instances of an E/R Diagram (section)
model: pro
rules: bullet definition math presentation short
Present the following. Use definition formal definition when it applies.
- Explains the concept of a database instance for an E/R diagram, which consists of a finite set of entities for each entity set and a set of tuples (the relationship set) for each relationship.
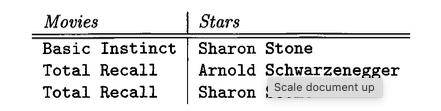
E/R diagrams provide a schema for a database. A specific collection of data that conforms to this schema is known as an instance of the database.
Definition: Instance of an E/R Diagram
An instance of a database corresponding to an E/R diagram consists of:
- For each entity set \(E\), a finite set of entities.
- For each relationship \(R\) connecting entity sets \(E_1, E_2, \ldots, E_n\), a finite set of tuples, called the relationship set. A tuple \((e_1, e_2, \ldots, e_n)\) is in the relationship set for \(R\) only if each \(e_i\) is an entity in the corresponding instance of entity set \(E_i\).
Entity Set Instance
For each entity set, the database instance contains a finite collection of entities. For an entity set
Movies, the instance is the set of all specific movie entities that exist in the database at a given time. Each such entity possesses particular values for its attributes.Relationship Set Instance
For each relationship, the instance is a finite set of tuples, where each tuple connects entities from the participating entity sets. These tuples represent the specific connections that exist in the data. For a relationship
Stars-inbetweenMoviesandStars, the relationship set is a collection of pairs \((m, s)\) where star \(s\) appears in movie \(m\).Visualization
While the components of a relationship set’s tuples are entities, not primitive values, it is convenient to visualize the set as a table. The columns correspond to the entity sets involved in the relationship, and each row represents one tuple from the relationship set.
- Version: 1
- Model: gemini-2.5-pro
- Created: 2025-09-09 21:34:46
- Duration: 14.83716893196106
- Cummulative cost: $1.88e-02
This is an instance of the relation Stars-in.
Multiplicity of Binary E/R Relationships
- Discusses restrictions on the multiplicity of relationships, such as many-one, one-many, one-one, and many-many.
- Explains the use of arrows in E/R diagrams to indicate a ‘many-one’ relationship (an entity is related to at most one entity in the set pointed to by the arrow).
#7
read: Section 4.1.6: Multiplicity of Binary E/R Relationships (section)
model: pro
rules: bullet definition math presentation short
Present the following. Use definition formal definition when it applies.
- Discusses restrictions on the multiplicity of relationships, such as many-one, one-many, one-one, and many-many.
- Explains the use of arrows in E/R diagrams to indicate a 'many-one' relationship (an entity is related to at most one entity in the set pointed to by the arrow).
Definition: Multiplicity of a Binary Relationship
Let \(R\) be a binary relationship connecting entity sets \(E\) and \(F\). The multiplicity of \(R\) is a constraint on the number of entities from one set that can be related to a single entity in the other set.
Many-One Relationship
A relationship \(R\) is said to be many-one from an entity set \(E\) to an entity set \(F\) if each entity in \(E\) can be connected by \(R\) to at most one entity in \(F\). Formally, for any entity \(e \in E\), the cardinality of the set \(\{f \mid f \in F \land (e, f) \in R\}\) is less than or equal to one. Note that an entity in \(F\) may be connected to many entities in \(E\).
One-Many Relationship
A relationship \(R\) is one-many from \(E\) to \(F\) if it is many-one from \(F\) to \(E\). That is, each entity in \(F\) can be connected by \(R\) to at most one entity in \(E\).
One-One Relationship
A relationship \(R\) is one-one if it is both many-one from \(E\) to \(F\) and many-one from \(F\) to \(E\). In a one-one relationship, an entity from either set can be connected to at most one entity of the other set.
Many-Many Relationship
A relationship \(R\) is many-many if it is neither many-one from \(E\) to \(F\) nor from \(F\) to \(E\). This is the most general type of relationship, with no multiplicity constraints.
Diagrammatic Notation
In an E/R diagram, a many-one relationship from entity set \(E\) to entity set \(F\) is denoted by an arrow on the edge from the relationship diamond to the rectangle for \(F\). The arrow points to the “one” side of the relationship, indicating that each entity in \(E\) is related to at most one entity in \(F\). Consequently, a one-one relationship is depicted with arrows pointing to both participating entity sets. A many-many relationship has no arrows.
- Version: 1
- Model: gemini-2.5-pro
- Created: 2025-09-09 21:35:00
- Duration: 13.811722993850708
- Cummulative cost: $1.70e-02
Multiway Relationships
- Covers relationships involving more than two entity sets (e.g., ternary relationships).
- Explains how arrows are used in multiway relationships to indicate functional dependencies.
#8
read: Section 4.1.7: Multiway Relationships (section)
model: pro
rules: bullet definition math presentation short
Present the following. Use definition formal definition when it applies.
- Covers relationships involving more than two entity sets (e.g., ternary relationships).
- Explains how arrows are used in multiway relationships to indicate functional dependencies.
Definition: Multiway Relationship
A relationship \(R\) among a collection of \(n\) entity sets \(\{E_1, E_2, \dots, E_n\}\), where \(n > 2\), is termed a multiway relationship. An instance of \(R\) is a relationship set, which is a collection of n-tuples \((e_1, e_2, \dots, e_n)\) such that each \(e_i \in E_i\).
A multiway relationship in an E/R diagram connects a diamond-shaped node to three or more rectangular entity set nodes.
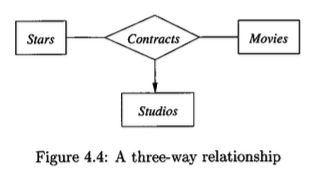
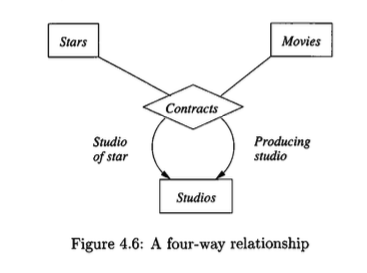
Ternary (three-way) or higher-degree relationships are less common than binary relationships but are sometimes necessary to model complex associations accurately. The
Contractsrelationship in Figure 4.4, involving a studio, a star, and a movie, is an example of a ternary relationship.The multiplicity of a multiway relationship can be indicated with arrows, which represent a functional dependency.
An arrow pointing from the relationship diamond to an entity set, say \(E_i\), signifies that for any given combination of entities from all other participating entity sets \(\{E_1, \dots, E_{i-1}, E_{i+1}, \dots, E_n\}\), there is at most one associated entity in \(E_i\). This can be expressed as a functional dependency: \[ (E_1, \dots, E_{i-1}, E_{i+1}, \dots, E_n) \rightarrow E_i \]
In the
Contractsexample of Figure 4.4, an arrow points to theStudiosentity set.This arrow indicates that for a given star and a given movie, there is only one studio with which that star has contracted for that movie. Therefore, the pair (star, movie) functionally determines the studio. No arrows point to
StarsorMovies, implying that a studio may contract with multiple stars for one movie, and a star may contract for multiple movies.
- Version: 1
- Model: gemini-2.5-pro
- Created: 2025-09-09 21:44:08
- Duration: 17.326938152313232
- Cummulative cost: $2.37e-02
Roles in Relationships
- Describes situations where an entity set appears more than once in a single relationship, requiring the use of labels called ‘roles’ on the edges to differentiate the functions of the entity set.
#9
read: Section 4.1.8: Roles in Relationships (section)
model: pro
rules: bullet definition math presentation short
Present the following. Use definition formal definition when it applies.
- Describes situations where an entity set appears more than once in a single relationship, requiring the use of labels called 'roles' on the edges to differentiate the functions of the entity set.
Definition: Role
In an Entity-Relationship model, a role is a label assigned to an edge connecting a relationship to an entity set. Roles are necessary when a single entity set participates in a relationship more than once, with each participation representing a different function.
An entity set may appear two or more times in a single relationship.
When an entity set participates multiple times, each line from the relationship diamond to the entity set rectangle represents a distinct role. To differentiate these participations, each line is labeled with a role name.
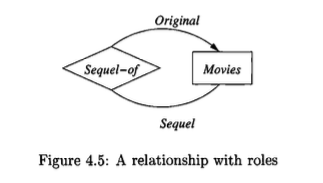
Consider a recursive relationship,
Sequel-of, which connects the entity setMoviesto itself.A relationship instance connects two movie entities, where one is the original film and the other is its sequel. To distinguish between the two, the lines connecting the
Sequel-ofrelationship to theMoviesentity set are labeled with the rolesOriginalandSequel. This clarifies that for any pair of movies in the relationship, one fulfills the role of the original and the other fulfills the role of the sequel.
- Version: 1
- Model: gemini-2.5-pro
- Created: 2025-09-09 21:44:18
- Duration: 9.452453136444092
- Cummulative cost: $1.13e-02
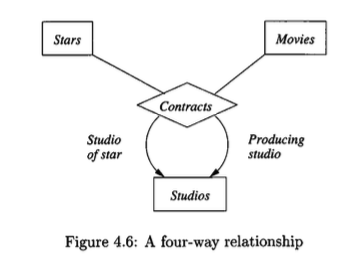
Note
The Studios entity set occurs twice in the ER-diagram:
- Studio of the star of the contract
- Studio of the movie of the contract
Attributes on Relationships
- Explains that attributes can be associated with relationships when the attribute is a property of the connection between entities, not of any single entity.
- Shows that placing attributes on relationships can be avoided by creating a new entity set to hold the attribute and including it in the relationship.
#10
read: Section 4.1.9: Attributes on Relationships (section)
model: pro
rules: bullet definition math presentation short
Present the following. Use definition formal definition when it applies.
- Explains that attributes can be associated with relationships when the attribute is a property of the connection between entities, not of any single entity.
- Shows that placing attributes on relationships can be avoided by creating a new entity set to hold the attribute and including it in the relationship.
It is sometimes necessary to associate attributes with a relationship rather than with an entity set.
An attribute is placed on a relationship when its value is a property of the combination of entities linked by the relationship, and not a property of any single entity. For instance, consider a
Contractsrelationship amongStars,Movies, andStudios. Thesalaryfor a contract depends on the specific star, for a specific movie, with a specific studio. It cannot be an attribute ofStarsalone (a star has different salaries for different movies) or ofMovies(different stars receive different salaries for the same movie).An attribute on a relationship is functionally determined by the participating entities.
Definition: Attribute on a Relationship
Let \(R\) be a relationship connecting entity sets \(E_1, E_2, \dots, E_n\). Let \(A\) be an attribute of \(R\). The value of \(A\) for a specific instance of the relationship, which is a tuple \((e_1, e_2, \dots, e_n)\) where each \(e_i \in E_i\), is determined by the entire tuple. This implies a functional dependency:
\[ \{E_1, E_2, \dots, E_n\} \to A \]
It is presumed that \(A\) is not functionally determined by any proper subset of these entity sets; otherwise, it would be more fitting to associate the attribute with the entity set(s) in that subset.
An attribute on a relationship can be converted into a new entity set.
It is never strictly necessary to place attributes on relationships. An alternative design is to create a new entity set to hold the attribute’s values. This new entity set then becomes a participant in the original relationship.
For example, the
salaryattribute on theContractsrelationship can be replaced by a new entity setSalarieswith the attributesalary. TheContractsrelationship is then redefined to be a four-way relationship amongStars,Movies,Studios, andSalaries. An arrow is drawn from the relationship to the newSalariesentity set, indicating that for any combination of a star, movie, and studio, the salary is uniquely determined.
- Version: 1
- Model: gemini-2.5-pro
- Created: 2025-09-09 21:44:33
- Duration: 15.368875980377197
- Cummulative cost: $1.79e-02
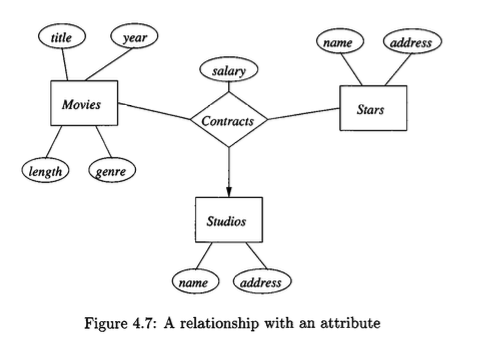
Each contract has a unique studio. Now, each contract also has a salary, which is an attribute of the relation.
Converting Multiway Relationships to Binary
- Describes a method to convert any multiway relationship into a collection of binary, many-one relationships by introducing a new ‘connecting entity set’ that represents the original relationship.
#11
read: Section 4.1.10: Converting Multiway Relationships to Binary (section)
model: pro
rules: bullet definition math presentation short
Present the following. Use definition formal definition when it applies.
- Describes a method to convert any multiway relationship into a collection of binary, many-one relationships by introducing a new 'connecting entity set' that represents the original relationship.
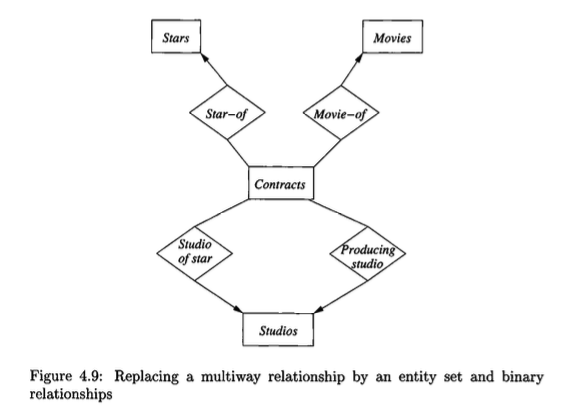
Definition: Connecting Entity Set
Let \(R\) be a multiway relationship among entity sets \(E_1, E_2, \ldots, E_n\). A connecting entity set is a new entity set whose instances correspond one-to-one with the tuples in the relationship set of \(R\). Each entity in the connecting entity set represents a specific tuple \((e_1, e_2, \ldots, e_n)\) where each \(e_i\) is an entity from the set \(E_i\).
Any relationship connecting more than two entity sets can be converted to a collection of binary, many-one relationships. This is achieved by introducing a new entity set to represent the multiway relationship itself.
Introduce a Connecting Entity Set
For a given multiway relationship, a new entity set is created. The entities within this set represent the tuples of the relationship set for the original multiway relationship. This new set is referred to as a “connecting entity set.”
Establish Binary, Many-One Relationships
For each entity set that participates in the original multiway relationship, a new binary relationship is introduced. This relationship connects the new connecting entity set to the original entity set.
Set Multiplicity Constraints
Each new binary relationship is defined as many-one, from the connecting entity set to the original entity set. An entity in the connecting set is linked to precisely one entity from each of the original participating sets. This constraint is represented by an arrow pointing to the original entity set.
Accommodate Multiple Roles
If an entity set participates in the multiway relationship in more than one role, then a separate binary, many-one relationship is created from the connecting entity set to that entity set for each role. Each such relationship is labeled to signify the specific role it represents.
- Version: 1
- Model: gemini-2.5-pro
- Created: 2025-09-09 21:44:49
- Duration: 15.43656611442566
- Cummulative cost: $1.72e-02
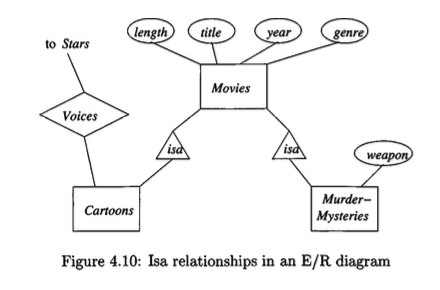
Subclasses in the E/R Model
- Introduces the concept of subclasses to represent special-case entities within an entity set that have unique attributes or relationships.
- Defines the
isarelationship, represented by a triangle, to connect a subclass to its superclass. - Explains that entities can have components in multiple entity sets within a subclass hierarchy, inheriting properties from all of them.
#12
read: Section 4.1.11: Subclasses in the E/R Model (section)
model: pro
rules: bullet definition math presentation short
Present the following. Use definition formal definition when it applies.
- Introduces the concept of subclasses to represent special-case entities within an entity set that have unique attributes or relationships.
- Defines the `isa` relationship, represented by a triangle, to connect a subclass to its superclass.
- Explains that entities can have components in multiple entity sets within a subclass hierarchy, inheriting properties from all of them.
Subclasses are special-case entity sets that contain entities with distinct properties not common to all members of a more general entity set (the superclass).
An entity set may contain specific members that possess unique attributes or participate in unique relationships. To model this, we define subclasses. For instance, within the general entity set
Movies, we might define subclasses such asCartoonsandMurder-Mysteries, each with its own special attributes or relationships.The connection between a superclass and its subclass is represented by a special
isarelationship.Definition:
isaRelationshipLet \(A\) and \(B\) be entity sets. The relationship “\(A\)
isa\(B\)” denotes that the set of entities constituting \(A\) is a subset of the entities constituting \(B\). For every entity \(e_A \in A\), there exists a corresponding entity \(e_B \in B\). This relationship is one-to-one; an entity in \(A\) inherits all attributes and relationships associated with its corresponding entity in \(B\). This relationship is represented graphically by a triangle pointing from the subclass to the superclass.An entity can be composed of components from multiple entity sets within an
isahierarchy, inheriting the properties of each.An entity is not confined to a single subclass. It may possess components in several entity sets, provided they form a valid path from a subclass up to the root of the hierarchy. For example, a movie that is both a cartoon and a murder mystery will have components in the
Movies,Cartoons, andMurder-Mysteriesentity sets. Consequently, it inherits the attributes and relationships from all three.
- Version: 1
- Model: gemini-2.5-pro
- Created: 2025-09-09 21:45:00
- Duration: 11.02611780166626
- Cummulative cost: $1.35e-02